Writing a successful tender for an EU project is a meticulous process that requires thorough preparation and a clear understanding of the requirements. This comprehensive guide provides a step-by-step approach to crafting a tender that stands out and meets all necessary criteria.
1. Understanding the Rationale of the Tender
Before diving into the specifics of writing the tender, it’s crucial to grasp the overall rationale behind the tendering process. This involves understanding what the contracting authority is looking for and ensuring that your submission aligns with these expectations. The tender process is divided into three main parts: Exclusion Criteria, Selection Criteria, and Award Criteria.
Exclusion Criteria
The exclusion criteria pertain to the administrative part of the tender. In this section, you must provide documents that prove your legal standing and compliance with various regulations. This includes evidence that your company is legally registered, not undergoing any resolution process, and is up-to-date with social security and tax obligations. While actual proof is required later in the process, during the tendering phase, you will need to fill out and sign a form attesting to your compliance.
Legal Documentation
To meet the exclusion criteria, you need to gather several key documents:
- Company Registration Documents: These include your company’s articles of incorporation, proof of registration with the relevant authorities, and any other documents that verify your legal status.
- Tax Compliance Certificates: Obtain certificates from your national tax authorities confirming that your company has no outstanding tax liabilities.
- Social Security Compliance Certificates: Similar to tax certificates, these documents confirm that your company has no outstanding social security contributions.
- Declarations of Non-Involvement in Criminal Activities: You will need to provide declarations confirming that neither your company nor its key personnel are involved in any criminal activities or are subject to any legal prohibitions that would prevent participation in the tender.
Attestation Forms
During the tendering phase, you will be required to complete and sign attestation forms. These forms serve as a preliminary declaration that your company meets all exclusion criteria. While the actual proof of compliance will be required later, these forms are a critical part of the initial submission.
Selection Criteria
The selection criteria are critical as they determine your eligibility to participate in the tender. This section evaluates both your financial and technical capacity.
Financial Capacity
The financial capacity assessment ensures that your company has the financial stability and resources to undertake the project. Key elements of this assessment include:
- Minimum Turnover Requirements: The tender will specify a minimum yearly turnover requirement. This ensures that your company can handle the financial risk associated with the contract. You may also need to demonstrate turnover related to similar services, proving past experience and capability.
- Profit and Loss Statements: Provide recent financial statements, including balance sheets, profit and loss statements, and cash flow statements. These documents should be audited and certified by a qualified accountant.
- Bank References: Obtain letters from your bank confirming your company’s financial stability and creditworthiness.
- Insurance Certificates: Provide proof of insurance coverage, including liability insurance, to demonstrate that your company can cover any potential risks associated with the project.
Technical Capacity
The technical capacity assessment evaluates your company’s ability to deliver the project based on past performance and available resources. Key elements of this assessment include:
- Relevant Experience: Describe similar projects you have completed, highlighting your expertise. This includes providing CVs of key personnel and evidence of partnerships with major vendors relevant to the project.
- Project Descriptions: Provide detailed descriptions of past projects, including objectives, outcomes, budgets, and timelines. Emphasize any similarities to the current tender requirements.
- Personnel Qualifications: Include CVs of key personnel who will be involved in the project, highlighting their relevant experience, qualifications, and expertise.
- Partnerships and Alliances: Provide evidence of partnerships with major vendors and subcontractors. Include details of any certifications or authorizations that demonstrate your ability to work with these partners.
- Resource Availability: Detail the resources you have available to deliver the project, including equipment, facilities, and technology.
Disqualification Risks
Failing to meet the financial or technical requirements will result in disqualification. Therefore, it is essential to thoroughly review the tender specifications and ensure that your submission addresses all criteria comprehensively.
Award Criteria
Once you pass the exclusion and selection criteria, your tender will be evaluated based on the award criteria. This section is where you earn points for the quality of your proposal, divided into technical and financial evaluations.
Technical Award
The technical award criteria assess the quality and feasibility of your technical proposal. This part of the evaluation typically carries the most weight, often around 70% of the total score. Key elements of the technical award criteria include:
- Understanding of Project Requirements: Demonstrate a clear understanding of the project requirements and objectives. Explain how your approach aligns with these requirements and addresses any potential challenges.
- Methodology and Approach: Provide a detailed methodology outlining how you plan to execute the project. Include a project plan with timelines, milestones, and deliverables.
- Innovation and Added Value: Highlight any innovative solutions or added value your proposal brings to the project. This could include new technologies, processes, or approaches that improve efficiency or outcomes.
- Risk Management: Outline your approach to identifying and mitigating risks associated with the project. Include a risk management plan with potential risks and corresponding mitigation strategies.
- Quality Assurance: Detail your quality assurance processes and procedures. Explain how you will ensure the project meets the required standards and specifications.
- Sustainability and Environmental Impact: Describe any measures you will take to minimize the environmental impact of the project and promote sustainability.
Scoring Example
If you score 82/100 in the technical evaluation and have the second-lowest price, your final score is calculated as follows:
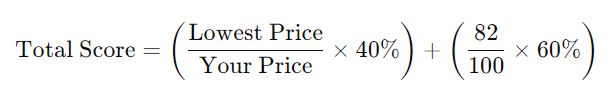
For instance, if the lowest price is 11 and yours is 12:
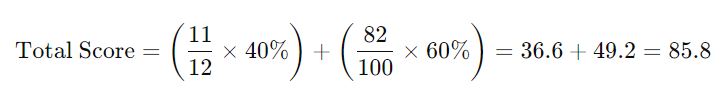
Financial Award
The financial award criteria assess the cost-effectiveness of your proposal. The weight of the financial part varies but is usually around 30%. This indicates the organization’s price sensitivity.
Importance of Pricing:
- Weight Allocation: Recognize how much weight the financials have in the overall score. This will guide how aggressively you need to price your offer.
- Detailed Breakdown: Provide a detailed breakdown of costs, including labor, materials, overheads, and any other expenses. Ensure that your pricing is competitive yet sustainable.
Precise Calculation:
- Accuracy: Be meticulous in your cost calculations. Ensure all expenses are accounted for, and your pricing is competitive without compromising quality.
- Justification: Where necessary, justify your costs to show they are reasonable and necessary for delivering high-quality work.
2. Preparing the Technical Tender
The technical tender details your proposed approach and methodology for the project. Here’s how to craft a compelling technical proposal:
Content Structuring
Compliance with Specifications:
- Structure: Follow the structure provided in the tender specifications. Create sections and paragraphs as outlined to ensure your proposal is comprehensive and organized.
- Alignment: Align your content with the evaluation criteria. Each section should provide evidence supporting the points where the evaluator will award marks.
Presentation:
- Clear and Concise Writing: Use clear language and avoid unnecessary jargon. Ensure your points are easily understood and directly address the criteria.
- Evidence and Examples: Provide concrete examples of past projects, detailed plans, and methodologies to demonstrate your ability to deliver.
Detailed Methodology
Project Plan:
- Timelines: Outline the project timeline, including key milestones and deliverables. Ensure that the timeline is realistic and achievable.
- Milestones: Define specific milestones that indicate progress and completion of key project phases.
Innovation and Value-Added Services:
- Innovation: Highlight any innovative approaches or technologies that you will use to enhance the project outcomes.
- Value-Added Services: Describe any additional services or benefits your proposal offers that go beyond the basic requirements.
Risk Management:
- Risk Identification: Identify potential risks associated with the project and their impact.
- Mitigation Strategies: Develop strategies to mitigate identified risks and ensure project success.
Quality Assurance:
- Processes: Detail your quality assurance processes, including how you will monitor and maintain quality throughout the project.
- Standards: Specify the standards and benchmarks you will use to measure quality.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact:
- Sustainable Practices: Describe any sustainable practices you will implement to minimize the environmental impact of the project.
- Environmental Benefits: Highlight the environmental benefits of your proposal.
3. Preparing the Financial Proposal
The financial proposal outlines the cost of the project. Here’s how to approach it:
Understanding Financial Sensitivity
Impact on Overall Score:
- Weight Allocation: Recognize how much weight the financials have in the overall score. This will guide how aggressively you need to price your offer.
- Detailed Breakdown: Provide a detailed breakdown of costs, including labor, materials, overheads, and any other expenses. Ensure that your pricing is competitive yet sustainable.
Precise Calculation:
- Accuracy: Be meticulous in your cost calculations. Ensure all expenses are accounted for, and your pricing is competitive without compromising quality.
- Justification: Where necessary, justify your costs to show they are reasonable and necessary for delivering high-quality work.
Cost Breakdown
Transparency:
- Detailed Breakdown: Provide a detailed breakdown of costs, including labor, materials, overheads, and any other expenses. This transparency helps the evaluators understand your pricing structure.
- Justification: Where necessary, justify your costs to show they are reasonable and necessary for delivering high-quality work.
Labor Costs:
- Hourly Rates: Detail the hourly rates for all personnel involved in the project. Include the number of hours each person will work and their respective costs.
- Total Labor Costs: Calculate the total labor costs by multiplying the hourly rates by the number of hours.
Material Costs:
- Material List: Provide a detailed list of materials required for the project, including quantities and unit costs.
- Total Material Costs: Calculate the total material costs by multiplying the unit costs by the quantities.
Overheads:
- Overhead Allocation: Allocate a percentage of overhead costs to the project. These costs include administrative expenses, utilities, and other indirect costs.
- Total Overheads: Calculate the total overhead costs and include them in the financial proposal.
Contingency Funds:
- Contingency Allocation: Allocate a percentage of the total project cost as a contingency fund. This fund covers unforeseen expenses and ensures project completion.
- Justification: Justify the contingency allocation by explaining potential risks and their financial impact.
Profit Margin:
- Profit Calculation: Calculate the profit margin as a percentage of the total project cost. Ensure that the profit margin is reasonable and competitive.
- Total Profit: Include the profit margin in the financial proposal.
Finalizing the Financial Proposal
Total Project Cost:
- Summarize Costs: Summarize all costs, including labor, materials, overheads, contingency funds, and profit margin.
- Total Cost Calculation: Calculate the total project cost by summing all the individual cost components.
Pricing Strategy:
- Competitive Pricing: Ensure that your pricing is competitive and reflects the quality and value of your proposal.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Highlight the cost-effectiveness of your proposal, emphasizing how it offers value for money.
Cost Justification:
- Detailed Justification: Provide a detailed justification for all costs, explaining why they are necessary for delivering high-quality work.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Conduct a cost-benefit analysis to demonstrate the value of your proposal relative to its cost.
4. Submission and Follow-Up
Once you have prepared both the technical and financial proposals, the next step is submission and follow-up.
Submission Process
Adherence to Deadlines:
- Deadline Compliance: Ensure that your tender is submitted before the deadline. Late submissions are typically not accepted.
- Timely Preparation: Start preparing your tender well in advance to avoid last-minute rushes and ensure timely submission.
Submission Format:
- Format Specifications: Follow the format specifications provided in the tender documents. This includes file formats, document structure, and any specific requirements.
- Document Packaging: Ensure that all documents are properly packaged and labeled as per the submission guidelines.
Electronic Submission:
- Online Portals: If the submission is electronic, ensure that you are familiar with the online submission portal and its requirements.
- Digital Signatures: Use digital signatures where required to authenticate your submission.
Follow-Up
Acknowledgment of Receipt:
- Confirmation: After submission, seek confirmation from the contracting authority that your tender has been received.
- Receipt Acknowledgment: Keep a copy of the acknowledgment receipt for your records.
Clarifications and Queries:
- Clarification Requests: If the contracting authority requests any clarifications or additional information, respond promptly and accurately.
- Ongoing Communication: Maintain open communication with the contracting authority throughout the evaluation process.
Feedback and Evaluation:
- Feedback Request: If your tender is not successful, request feedback to understand the reasons and improve future submissions.
- Evaluation Criteria: Use the feedback to assess how well your tender met the evaluation criteria and identify areas for improvement.
5. Best Practices for Successful Tenders
To increase your chances of success, follow these best practices when preparing and submitting your tender:
Thorough Preparation
Early Start:
- Early Planning: Start preparing your tender as soon as the opportunity is announced. This gives you ample time to gather information, prepare documents, and address any issues.
- Team Coordination: Coordinate with your team and allocate responsibilities to ensure all aspects of the tender are covered.
Detailed Analysis:
- Tender Documents: Thoroughly read and analyze the tender documents to understand all requirements and criteria.
- Requirement Checklist: Create a checklist of all requirements and criteria to ensure nothing is overlooked.
Clear and Concise Writing
Plain Language:
- Simple Language: Use plain language and avoid jargon. Ensure that your proposal is easy to read and understand.
- Direct Address: Directly address each requirement and criteria in your proposal.
Proofreading:
- Thorough Review: Proofread your proposal multiple times to eliminate any errors or inconsistencies.
- Peer Review: Have your proposal reviewed by colleagues to get feedback and identify any areas for improvement.
Strong Evidence and Justification
Concrete Examples:
- Past Projects: Provide concrete examples of past projects that demonstrate your experience and expertise.
- Quantifiable Results: Use quantifiable results and metrics to showcase the success of past projects.
Detailed Justifications:
- Cost Justifications: Provide detailed justifications for all costs, explaining why they are necessary.
- Methodology Justifications: Justify your methodology and approach, highlighting how they meet the project requirements.
Competitive Pricing
Market Research:
- Competitive Analysis: Conduct market research to understand the competitive landscape and pricing strategies.
- Benchmarking: Benchmark your pricing against competitors to ensure it is competitive.
Value Proposition:
- Highlight Value: Emphasize the value your proposal offers, highlighting any unique benefits or advantages.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Provide a cost-benefit analysis to demonstrate the value of your proposal relative to its cost.
Compliance and Accuracy
Checklist Compliance:
- Compliance Checklist: Use a compliance checklist to ensure that all requirements and criteria are met.
- Document Accuracy: Verify the accuracy of all documents and information provided in your tender.
Regulatory Compliance:
- Regulatory Requirements: Ensure that your proposal complies with all relevant regulatory requirements and standards.
- Legal Review: Have your proposal reviewed by legal experts to ensure compliance with all legal requirements.
Effective Communication
Clear Communication:
- Communication Plan: Develop a communication plan to ensure clear and effective communication with the contracting authority.
- Clarification Queries: Proactively seek clarifications from the contracting authority if any requirements or criteria are unclear.
Ongoing Engagement:
- Follow-Up: Follow up with the contracting authority after submission to confirm receipt and address any queries.
- Feedback Request: Request feedback after the evaluation to understand the strengths and weaknesses of your proposal.
Conclusion
Successfully writing an EU tender requires thorough preparation, attention to detail, and a strategic approach. By understanding the exclusion, selection, and award criteria, and carefully crafting your technical and financial proposals, you increase your chances of winning the tender. Always align your submission with the tender specifications and evaluation criteria, and ensure that both your technical approach and pricing are competitive and well-justified.
Remember to start early, coordinate with your team, and follow best practices for successful tenders. By doing so, you can create a compelling and competitive proposal that stands out in the evaluation process.


